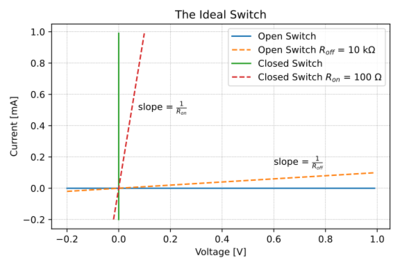
CoE 197U The MOS Switch
Revision as of 10:18, 8 March 2021 by Louis Alarcon (talk | contribs)
Contents
Levels of Abstraction
As integrated circuits continue to increase in complexity and sophistication, the amount of information and information processing needed to design, fabricate, and test these ICs also increase. Without a way to organize this information, engineers can be easily overwhelmed. One strategy is to define levels of abstraction, where we partition the information, and use only the components needed for a particular task. This strategy can then be used to create models appropriate for a certain objective.
We create models to allow us to predict the behavior of a circuit or system.
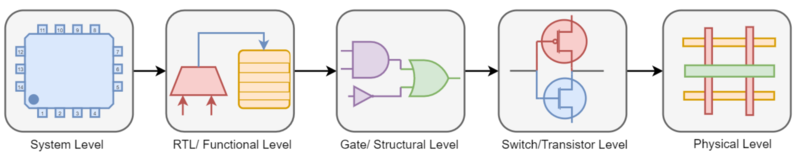 Figure 1: Levels of abstraction[1]. |
What is a Transistor?
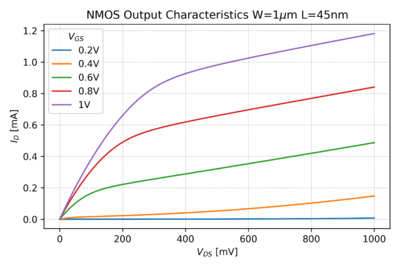 Figure 2: The 45nm NMOS PTM[2] output characteristics. |