Shannon's Communication Theory
Revision as of 15:56, 14 September 2020 by Louis Alarcon (talk | contribs)
Contents
A First Look at Shannon's Communication Theory
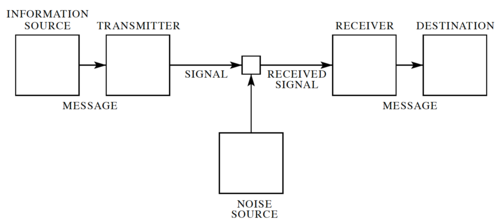
Figure 1: A general communication system[1].
In his landmark 1948 paper[1], Claude Shannon developed a general model for communication systems, as well as a framework for analyzing these systems. The model has three components: (1) the sender or source, (2) the channel, and (3) the receiver or sink. The model also includes encoding and decoding blocks, as well the noise of the channel, as shown in Fig. 1.