Difference between revisions of "CoE 197U Scaling"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Why is this paper and the graph in Fig. 1 important? Gordon Moore's prediction, also known as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore%27s_law Moore's Law], has reflected and, more importantly, driven the steady and rapid progress in computing technology. | ||
== Evolution of Complexity == | == Evolution of Complexity == | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 22 February 2021
Contents
Moore's Law
In 1965, Gordon Moore published a 4-page paper entitled "Cramming more components onto integrated circuits"[1], where he predicted that the number of components in an integrated circuit will increase by a factor of two every year, as shown in Fig. 1. Note that he based his extrapolation on just 4 data points!
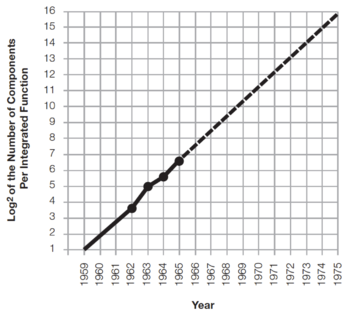 Figure 1: Gordon Moore's 1965 prediction[1]. |
Why is this paper and the graph in Fig. 1 important? Gordon Moore's prediction, also known as Moore's Law, has reflected and, more importantly, driven the steady and rapid progress in computing technology.
Evolution of Complexity
Transistor Count
Frequency
Power Dissipation
Challenges in Digital Design
Why Scale?
The Cost of Integrated Circuits
Non-Recurrent Engineering Costs
Recurrent Costs
Yield
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Gordon E Moore, Cramming more components onto integrated circuits, Electronics, Volume 38, Number 8, April 19, 1965 (pdf)