Difference between revisions of "Passive CMOS Devices"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Silicide cmos.png|thumb|500px|Figure 3: Silicide layers on diffusion and polysilicon layers to reduce the effective sheet resistance<ref>Krishna Saraswat's [https://web.stanford.edu/class/ee311/NOTES/Silicides%20&%20Metal%20gate%20Slides.pdf slides] on Polycides, Salicides andMetals Gates.</ref>.]] | ||
| + | In a CMOS process optimized for digital circuits, the low sheet resistances of the semiconductor layers are due to a low-resistance silicide layer deposited on top of the semiconductor layer, as shown in Fig. 3. In analog CMOS processes, we are usually given the option to place a silicide block, i.e. to prevent the silicide layer from being deposited on specific locations on the die. | ||
== Capacitors == | == Capacitors == | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 20 September 2020
Passive devices such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, are commonly used in biasing circuits, feedback networks, and signal or energy storage blocks. However, these passive devices, when built on fabrication processes that are optimized for transistors, may have characteristics different from their ideal or discrete counterparts. In this module, we examine the behavior of passive devices built alongside CMOS transistors.
Contents
Resistors
In standard digital CMOS processes, there is usually no provision for high resistance layers, since resistances are typically deemed bad for digital circuits. But in analog design, we often need well-controlled resistors, with relatively large resistance values. In order to evaluate if a particular layer could be used as to build a resistor, we look to their sheet resistance. Recall that for a resistor:
-
(1)
-
Where is the sheet resistance of the layer, is the resistivity of the material, is the length along the direction of the current, and , is the cross sectional area normal to the current flow, which is equal to the product of the layer thickness, and is the width of the layer perpendicular to the current flow. The table below shows indicative values of the common conductive layers in a CMOS process:
| Layer | Sheet Resistance |
|---|---|
| Metal | |
| Polysilicon | |
| or Diffusion | |
| -well |
An illustrative cross-section of resistors using these layers are shown in Figs. 1 and 2.
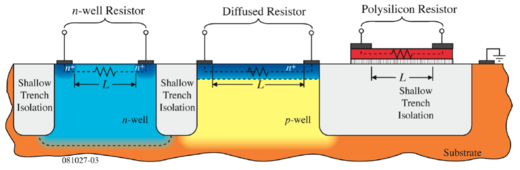 Figure 1: Resistors built using semiconductor layers[1]. |
 Figure 2: Resistors built using metal layers[1]. |
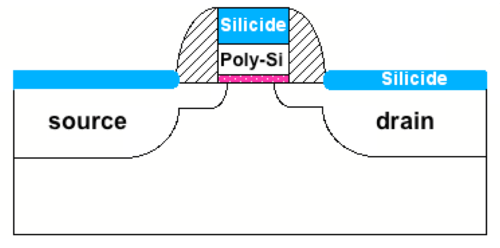
In a CMOS process optimized for digital circuits, the low sheet resistances of the semiconductor layers are due to a low-resistance silicide layer deposited on top of the semiconductor layer, as shown in Fig. 3. In analog CMOS processes, we are usually given the option to place a silicide block, i.e. to prevent the silicide layer from being deposited on specific locations on the die.
Capacitors
Inductors
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Phillip Allen's slides on Deep Submicron CMOS Technologies
- ↑ Krishna Saraswat's slides on Polycides, Salicides andMetals Gates.












